Hair Knowledge
Hair Thickness and What You Need to Know
Hair thickness not only affects the natural appearance of the hair, but is also a key factor when choosing the right product. So what is hair thickness? How to measure it and what factors affect it? Let’s find out with N Hair through the article below.
1. What is Hair Thickness?
Hair thickness (also known as hair diameter) is the horizontal dimension of a single hair, usually measured in micrometers (µm) or millimeters (mm). Many people confuse “thickness” with “hair density”, but they are two different concepts:
- Thickness: Refers to the size of individual hairs.
- Hair density: The number of hairs on a given area of the scalp.
Hair thickness can vary depending on race, genetics, age, and environmental factors. Understanding hair thickness helps you choose the right type of hair extensions, care products and styling techniques.
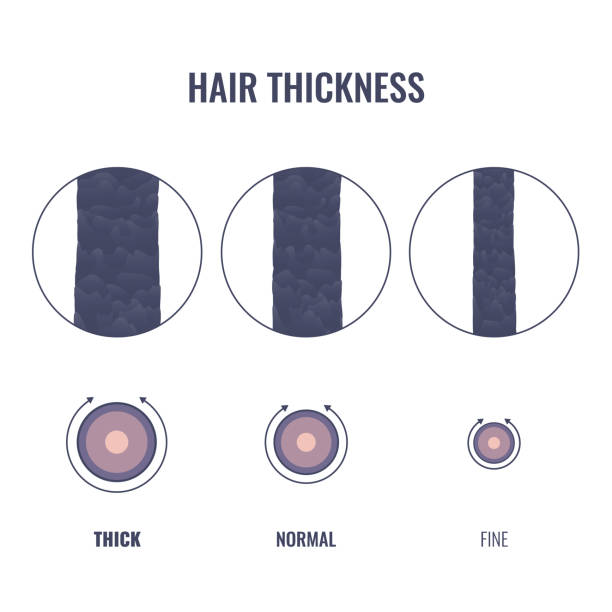
According to European standards, hair is considered thin if it has a diameter of 40 to 60 µm, hair with a diameter of 60 to 80 µm is considered normal and hair is thick if it has a diameter of over 80 µm. Asian (dark) hair is usually much thicker than European hair, with an average diameter of 80 – 120 µm.
| Hair Source | Average hair thickness (µm) |
|---|---|
| Vietnam | 80–100 |
| Indian | 90–110 |
| China | 80–100 |
| Brazil | 100–120 |
| Russia | 70–90 |
Note: The above values are for reference only and may vary depending on many factors.
2. Why need to understand hair thickness
Understanding hair thickness not only helps you determine your hair type, but also plays a decisive role in choosing the right products, care techniques, and styling styles. Here are some specific benefits:
2.1. Choosing the right hair care products
- For thin hair, you need to use a mild shampoo that increases volume and contains nourishing ingredients such as biotin or collagen.
- Thick hair needs products that help soften and deeply moisturize to avoid frizz or dryness.
- Choosing the wrong product is not only wasteful but also damages the hair structure in the long run.
2.2. Easier and more suitable styling
- Thick hair holds its shape well, making it easy to curl, braid, or curl in large waves.
- Thin hair needs volumizing techniques (using mousse, rollers, creating light waves) to look thicker and more voluminous.
- Professional hairdressers often rely on thickness to advise on hairstyles that suit the client’s face and hair type.
2.3. Care and safe chemical treatment
- Thin hair is easily damaged when dyeing, straightening, or curling because the cuticle is less protected.
- Thick hair requires longer chemical treatment time but is more heat resistant.
- Knowing the thickness of the hair helps hairdressers adjust the chemical retention time and the appropriate temperature of the curling/straightening iron.
2.4. Predict the health of the hair and scalp
- Hair that suddenly becomes thin and weak can be a warning sign of nutritional deficiencies, stress, or hormonal disorders.
- By analyzing hair thickness, you can monitor and adjust your lifestyle, diet, and living habits accordingly.
2.5. Choosing hair extensions and the correct hair extension technique
- People with thin hair should choose light hair extensions, avoid thick extensions that weigh down the scalp and cause real hair loss.
- People with thicker hair can use braids, weaves or keratin extensions without causing damage.
3. How to Measure Hair Thickness
There are many simple methods to measure or estimate hair thickness:
- Compare with A4 paper: Paper is usually ~70 microns thick. If the hair is thinner than the height, it is fine hair; if it is similar or thicker, it is medium to thick hair.
- Feel by hand: Hold a hair strand between two fingers. If it is difficult to feel, the hair is thin; if if clear, it is thick.
- Compare the thread: If the hair strand is close to the thread, it is thick hair.
- Specialized tools: Use a digital caliper or microscope to measure accurately.

4. Factors Affecting Hair Thickness
4.1. Genetic factors
This is the main factor that determines the structure and thickness of hair strands. If parents have thick and strong hair, their children often inherit this trait. However, genes not only determine the thickness but also affect the shape of the hair strands (straight, curly, wavy) and the hair growth cycle.
4.2. Nutrition
Healthy hair needs to be nourished from the inside. Lack of essential nutrients such as:
- Protein (main component of hair),
- Biotin (vitamin B7),
- Vitamins A, E, D, iron, zinc … can all make hair weak, dry, brittle and thinner. An unbalanced diet or sudden weight loss also negatively affects hair thickness.
4.3. Environmental and chemical impacts
- Air pollution, UV rays, high temperatures from dryers, irons, or sunlight can damage the hair cuticle, causing hair to become thinner and weaker.
- Chemicals in dyes, perms, and straighteners, if used regularly and improperly, will destroy the keratin layer that protects the hair, causing the hair to become brittle and lose its natural thickness over time.
4.4. Stress and hormones
Prolonged stress can disrupt hormones and affect the hair growth cycle, causing hair to stop growing and fall out. Hormonal changes such as postpartum, menopause, puberty, or thyroid disorders are also often accompanied by a noticeable thinning and thinning of hair.
4.5. Hair care habits
- Washing your hair incorrectly (too often or using harsh products),
- Brushing your hair when it is wet, tying your hair too tightly,
- Using the wrong type of comb or washing your hair with hot water… are all habits that can cause hair to break easily, thereby making your hair thinner over time. In addition, using the wrong care products can also weigh down your hair or clog your hair follicles, affecting its thickness.
5. Hair Thickness Restoration Solutions
5.1. Improve your diet
- Add foods rich in protein (eggs, fish, soybeans),
- Eat lots of dark green vegetables, seeds, whole grains,
- Maintain adequate water intake every day,
- You can supplement with biotin, collagen, zinc after consulting your doctor.
5.2. Use specialized hair care products
- Choose sulfate-free shampoos and conditioners that are gentle and contain hair growth stimulating ingredients such as: biotin, caffeine, grapefruit extract, argan oil…
- Use serum or essential oils to nourish strong hair from root to tip.
- Avoid styling products containing alcohol or high heat agents.
5.3. Regular scalp massage
Gently massaging the scalp for 5–10 minutes every day will help:
- Increase blood circulation,
- Stimulate hair follicles to grow,
- Support thicker and healthier hair growth.
5.4. Change your styling habits
- Avoid tying your hair too tightly or tying it up in a high bun regularly,
- Limit the use of heat styling tools (dryers, straighteners) – or use a combination of heat protection sprays,
- Brush your hair gently with a wide-tooth comb, especially when your hair is wet.
5.5. Cosmetic and medical treatments
If your thinning hair is severe, you can consider the following specialized methods:
- PRP (platelet-rich plasma) treatment to regenerate hair follicles,
- Bio-hair transplant or laser therapy to stimulate hair growth,
- Artificial hair extensions – the ideal choice if you want thick hair immediately without having to wait for it to grow back naturally.
6. Conclusion
Understanding hair thickness is the first step to caring for and choosing the right hair extensions. Whether you are a customer or a technician, properly analyzing the thickness will help the beauty process be more effective, safer and more durable over time.





